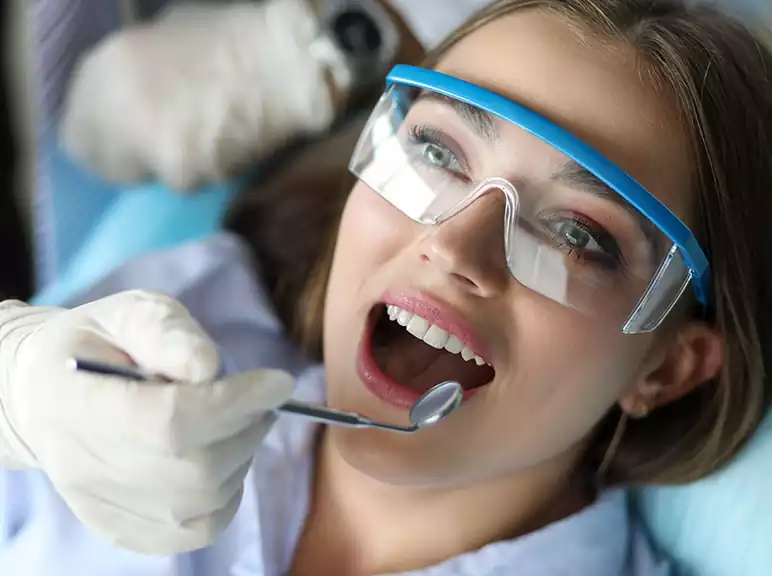
Dental Restoration
Restorations is a way the dentist can replace or restore missing teeth or missing parts of the teeth. Examples are fillings, crowns, bridges, implants and dentures. The structure of the tooth may be missing due to decay, deterioration (weakening) of the restoration, or fracture of the tooth. Restorations include the following:
- Fillings are the most common kind of dental restoration. Teeth may be filled with silver amalgam, gold or tooth-coloured plastic and glass materials popularly known as composite resin fillings.
- Crowns are caps that are tooth-shaped which is placed over a tooth to restore its shape and size, strength and appearance, to hold a bridge in place, or to cover a dental implant. Teeth often need to be reduced evenly around the tooth so that the crown restores the size and shape of the tooth correctly. It is a long process and can involve an impression that has been sent to the laboratory, with a temporary filling/crown in the meantime. Some of the offices have technology that sends a digital impression to a milling machine that produces a crown in the office, sometimes on one visit.
- Bridges are false teeth which are designed to “bridge” the gap made by 1 or more missing teeth. Bridges may be anchored on either side by crowns and cemented permanently into the place.
- Implants are replacement tooth roots. It is a small post made of metal (typically titanium or a titanium mixture) which are placed into the socket of the bone where teeth are missing. Implants may need an attachment known as an abutment that will act like a crown preparation. It is covered with a crown.
- Dentures are replacement for missing teeth and surrounding tissues. They are removable They are made of acrylic resin, at times combined with metal attachment. Complete dentures will replace all teeth. Partial dentures are regarded when some natural teeth remain and are retained by metal clasps attached to the natural teeth.
A filling is a material that our dentists use to fill a cavity after they remove any tooth decay.
To fill a tooth, our dentist will:
- Numb the teeth, tongue, gums and surrounding skin. Our dentist will then put a substance which feels like jelly directly on the area to begin the numbing process, then inject an anaesthetic to finish it.
- At times use a small sheet of rubber on the metal frame (rubber dam) to aim the decayed tooth and to prevent tooth chips and liquid from entering the mouth and throat.
- Take out all the decay as well as replace it with a filling.
Fillings can be prepared from many kinds of material. Talk to our dentist about which type will be suitable for you.
- Amalgam is the most straightforward material for our dentist to use. It is the quickest and least costly option. Amalgam is a combination of mercury, tin, silver, or other metals.
- Composite resins are tooth-coloured fillings. Composite resin is simpler than gold for a dentist to work with and usually is less costly than gold.
- Ionomers are tooth-coloured materials which dentists often use for time cavities or cavities between teeth. A few ionomers release little amounts of fluoride, that may help you if you usually get cavities.
- Gold is expensive, and it is usually difficult for the dentist to work with it. It makes the procedure longer and cost more.
- Ceramics are costly tooth-coloured fillings. It requires special equipment and may require dental lab support. You may need several appointments.
What to Expect After Treatment?
After the dentist has filled the cavity, the gums and lips may remain numb for a few hours until the numbing medicine is gone. To avoid any injuries in the mouth, be careful not to chew on the numb cheek or lip.
Why Is It Done?
You will need a filling when the tooth decay has caused a cavity to form on the tooth surface. If you wouldn’t get a filling, the cavity is going to get worse. It can cause discomfort and then abscess. It can lead to even severe problems, for example, bone loss.
How Well It Works?
The filling repairs the tooth and prevents the decay of the tooth. You may also need to replace the worn-out filling over a long period. Your tooth may be sensitive to cold and heat for days to weeks after filling. Talk to our dentist about toothpastes that may help you with your discomfort. Tell our dentist if your teeth are too sensitive after filling, because you can usually deal with this problem.
Risks
There is almost no risk that a cavity will be filled. If you have difficulties with your heart, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics before a dental procedure. Some procedures may cause bacteria in the mouth to travel through the bloodstream and cause an infection in other parts of the body. Antibiotics lower your risk of developing an infection in your heart called endocarditis.
What to Think About?
It is essential to start treatment before the tooth decay gets worse. More severe decay can lead to pain and tooth loss and may require costly crown, root canal removal, or tooth removal (extraction). In some instances, dentists use a laser system to remove the tooth decay and to prepare the tooth for filling. Laser treatment is a relatively new option for dental treatment and may not be available in your area.