Childhood Obesity
Obesity: It is described as a condition in which the natural energy reserve collected in fatty tissues of humans and other mammals is enhanced to the point where it is connected with certain conditions of health or increased mortality. It’s becoming a cosmetic issue, too, and people yearn for weight loss.
Childhood Obesity
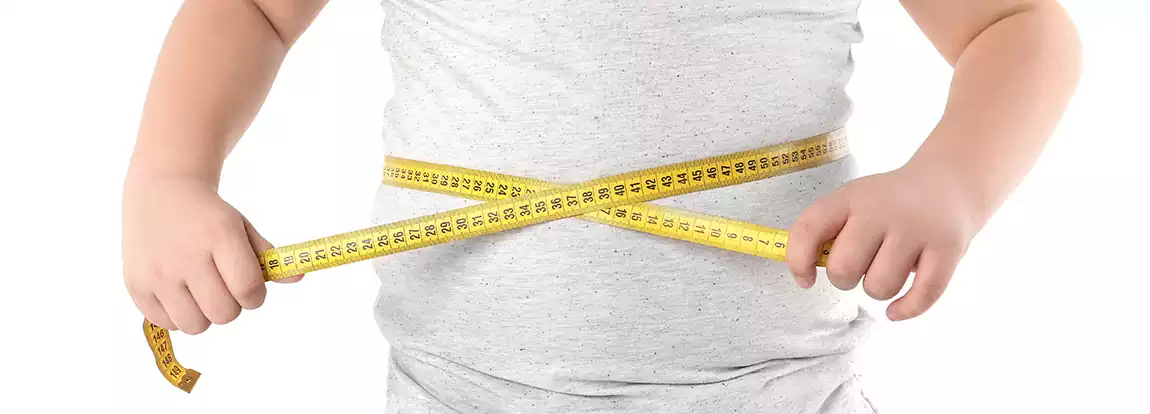
Childhood obesity has become a severe medical condition affecting children and adolescents. It takes place when a child is well above average weight because of his or her height and age. Childhood obesity is particularly troubling because excess weight often pushes children to health issues once confined to grown-ups, such as high blood pressure, diabetes and high cholesterol. Childhood obesity can also lead to low self-esteem and depression. One of the best strategies to minimize childhood obesity is to improve your entire family’s diet and exercise habits.
Obesity is both a specific medical condition and is increasingly seen as a severe public health problem. Increased body weight has been shown to predispose people to different diseases.
Being obese or overweight is not the same thing. An obese individual has a lot of extra body fat, not just a few extra kilos/pounds. Individuals who are obese are very overweight and at risk of serious health conditions.
Metrics
Obesity is generally evaluated by measuring BMI (Body Mass Index), girth circumference and risk factor assessment.
Causes of Obesity
Overeating
When food energy intake exceeds energy consumption, fat cells (and also, to some extent,
muscle and liver cells) throughout the body consume energy and store it as fat. Thus, when energy consumption increases the requirement, it leads to obesity.
Additional factors causing obesity
- Stress
- Genetic disorders
- Underlying illness (such as hypothyroidism)
- Eating disorders (such as Binge eating disorder)
- Weight cycling – repeated efforts to do dieting to lose weight
- Certain medications (such as antipsychotics)
- Sudden smoking cessation
- Sedentary lifestyle
- A high glycaemic diet
- Insufficient sleep
Global Obesity Statistics
Since the mid-seventies, the existence of overweight and obesity has increased sharply for both adults and children universally. Some data show that the prevalence of obesity among adults aged 20–74 years increased from 15.0% (in 1976–1980 survey) to 32.9% (in the 2003–2004 study). The world average is 14.1%, with the United States of America, Mexico, United Kingdom, Slovakia, Greece, Australia, New Zealand, Hungary, Luxembourg and the Czech Republic standing out by far the most obese nations.
The two surveys also indicate an increase in weight among children and adults. For children aged 3–5 years, the prevalence of overweight increased from 5.0% to 13.8%; for those aged 6–12 years, the prevalence increased from 6.5% to 18.9%; and for those aged 13–19 years, the prevalence increased from 5.0% to 17.5%. These rising rates are causing concern because of their impact on the health of the world population. Overweight or obese increases the risk of critical disorders and diseases and health conditions, such as the following:
- Hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoarthritis
- Dyslipidaemia (such as high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels)
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Sleep apnoea and respiratory problems
Types of Obesity
The distribution of body fat in the body is identified as one of the2 types of obesity android & gynoid.
Android: – The type of Android obesity is like the shape of an apple. The shoulders, arms, face, neck, chest and upper part of the abdomen are bloated. The stomach gives a stiff appearance, as do the arms, shoulders, and breasts.
Gynoid: – The lower part of the body has additional flesh in this type. This type of obesity is also prevalent to both sexes, although females are more affected. The kind of Gynoid obesity is similar to pears. The flesh in the abdomen, thighs, buttocks and legs is somewhat flabby. Usually, the face and neck give a healthy appearance. The cheeks may also be drawn in some people.
The third type: – Apart from android and gynoid, there is another type of obesity. Some individuals do not belong to any of the types of obesity mentioned above. Their whole body looks like a barrel from head to toe. Their gait is more about rolling than walking. The fat tissues in their bodies hinder the movement of all internal organs and therefore affect their rapid functioning. For them, any exercise is challenging because of the enormous size of the body. So that person should follow a strict diet and do a lot of exercise.
Treatment of Obesity
Anti-obesity drugs
Fluoxetine, Orsilat and Sibutramine may lose weight for 13 to 50 weeks, but the amount of loss is moderate, and the long-term health benefits remain unclear. Orlistat plays a role in dietary / exercise-resistant obesity by inhibiting pancreatic lipase and reducing intestinal fat absorption. Sibutramine is an anorexic, but its health safety factor remains uncertain.
Surgery for Obesity
Bariatric surgery – Weight loss surgery is the use of surgical procedures in the treatment of obesity by dropping the volume of the stomach, producing an earlier sensation of satiety (by adjustable gastric bandage and vertical bandage) or by reducing the length of the intestine and thus directly reducing absorption (gastric by-pass surgery). Band surgery is reversible, but others aren’t.
Homoeopathic medicine for weight loss
Homoeopathy is treating the person as a whole. It means that homoeopathic remedy focuses on the patient as an individual, and his or her pathological condition. Homoeopathic medicine for weight loss is chosen after a complete individualization and case-analysis, including the patient’s medical history, physical and mental constitution, etc.
Miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is most often taken into account in the treatment of chronic conditions. The following medicines indicate therapeutic affinity, but this is not a complete and definitive guide to the treatment of obesity or weight loss.
Homoeopathic Remedies for Obesity / Weight Loss
- Calcarea-carb
- Ferrum met
- Graphitis
- Phytolacca
- Thyroidinum
- Antim-crud
- Fucus religoisa
- Phosphorus
- Kali-bi chrome
- Kali-carb
- Pulsatilla
- Senega